The widespread distribution of disinformation across digital platforms, also due to the development of various AI tools, has significantly challenged manual fact-checking methods. As a result, fact-checkers increasingly rely on artificial intelligence in their daily tasks to process the vast volume of disinformation circulating in the information ecosystem. Several companies have developed AI-based tools offering solutions to the challenges of manual fact-checking, a process that can take a lot of time and resources.
Ways AI can automate fact-checking
By automating various tasks, artificial intelligence can significantly increase the speed, scalability and accuracy of fact-checking. One approach is the use of natural language processing and content analysis to identify the main claims in a text, detect contradictions within it, and uncover logical errors. AI tools can also analyze whether the text employs emotional or biased language. Another approach involves developing models capable of identifying specific phrases or writing styles commonly used in disinformation. This would enable the analysis of large sets of data, allowing artificial intelligence to detect anomalies within that data. AI can also be used to analyze audio-visual content. Artificial intelligence-based tools can examine photos to verify whether they have been manipulated or fabricated.
AI-powered tools to combat disinformation
Various companies are already developing new tools and applications that use artificial intelligence to help with verification. Some of the text verification tools currently used by fact-checkers worldwide include ClaimBuster, MyAIFactChecker, and GPTzero. These are all free, while other tools, such as Perspective API developed by Google or Factiverse, are paid.
ClaimBuster allows for the quick identification of various claims circulating on the Internet. Similar in function, MyAIFactChecker offers a broader range of services, including sentiment analysis and resource classification. Specialized tools are now available to identify texts generated by artificial intelligence, as another way to detect disinformation produced using artificial intelligence. One such tool is GPTZero, which detects whether a piece of content is AI-generated, whether it is an article or social media bot comments.
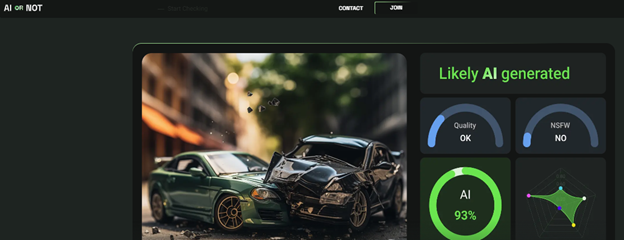
In addition to text verification, tools based on artificial intelligence are already aiding in the verification of audio, photos, and videos. AI or NOT is a tool that helps verify photos and audio generated by artificial intelligence. However, when it comes to AI-generated videos, such as deepfakes, no tool currently offers effective detection, as existing solutions lack the necessary accuracy for full reliance. To address this, I have developed the model of DeepFakeShield which outlines six steps to help anyone verify whether a video is a deepfake.

In all this development, it's important to consider the limitations of AI tools. For example, AI algorithms are trained on specific datasets, making the choice of data training crucial. Another key limitation is language, as some AI tools are only trained in certain languages, which can hinder their effectiveness in others.
The rapid development of technology and artificial intelligence does not diminish the importance of human judgment in the verification process. Instead, AI tools enable fact-checkers to identify misinformation or manipulation more quickly. While AI-based tools are a valuable asset, human oversight and judgment remain crucial in the verification process. The combination of human expertise and AI tools helps combat disinformation more effectively and efficiently.
To better understand the role of artificial intelligence, both in the verification process and in everyday life, education on AI is essential. AI literacy will support the development, implementation, and ethical use of AI. Irresponsible use of artificial intelligence only exacerbates problems in the information environment. To mitigate this, steps should be taken to educate people about AI's role in general, and its specific role in fact-checking.
Background illustration: Generated by the author with an AI tool.